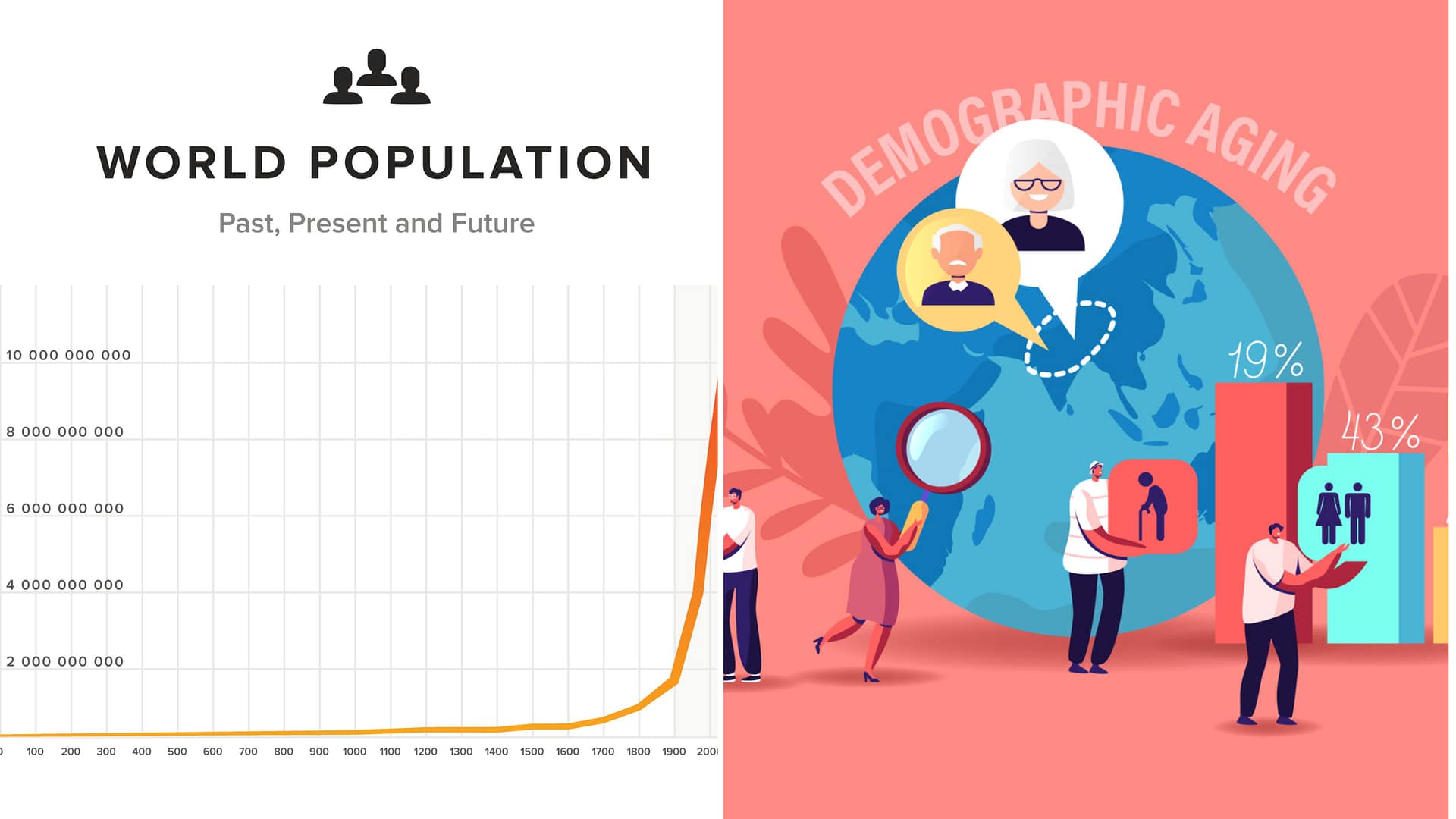
The world’s population is expected to start declining from 2046, according to comments by Russian presidential aide Maxim Oreshkin, signaling a major demographic shift with far-reaching economic and social implications.
The projection underscores growing concerns among policymakers and economists about aging societies, shrinking workforces, and long-term growth constraints across both developed and emerging economies.
Key Takeaways
- Global population growth may reverse starting in 2046.
- The outlook was highlighted by Maxim Oreshkin.
- Demographic decline could pressure labor markets and growth.
- Aging populations are becoming a central policy challenge.
Oreshkin Highlights Demographic Turning Point
Speaking on long-term global trends, said that the world population is projected to begin shrinking from 2046. His remarks, cited by Russian media, point to declining birth rates and longer life expectancy as key drivers of the shift.
Such a turning point would mark the first sustained global population decline in modern history.
Economic Implications of a Shrinking Population
Economists warn that population decline can weigh on economic growth by reducing labor supply and increasing dependency ratios. Fewer working-age individuals may place added strain on pension systems, healthcare spending, and public finances.
Analysts referenced by note that countries failing to adapt productivity and migration policies could face prolonged periods of slower growth.
Aging Societies and Labor Market Pressures
Many major economies are already experiencing aging populations, with fertility rates below replacement levels. As these trends deepen, competition for skilled labor is expected to intensify, potentially reshaping global migration patterns.
Coverage by has previously highlighted that demographic headwinds are becoming as influential as traditional macroeconomic factors in long-term planning.
Policy Responses in Focus
Governments may increasingly turn to policies aimed at boosting birth rates, extending working lives, or leveraging automation and artificial intelligence to offset labor shortages. Immigration is also likely to remain a sensitive but critical tool for sustaining economic activity.
The effectiveness of these measures will vary widely depending on political, cultural, and economic conditions.
What To Watch Next
- Updated population projections from international institutions.
- Policy responses to aging and declining workforces.
- Long-term impacts on global growth and labor markets.
This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice.